Train Your First Agent
ReinforceNow supports training agents. With agents we mean large language models that can invoke tools.
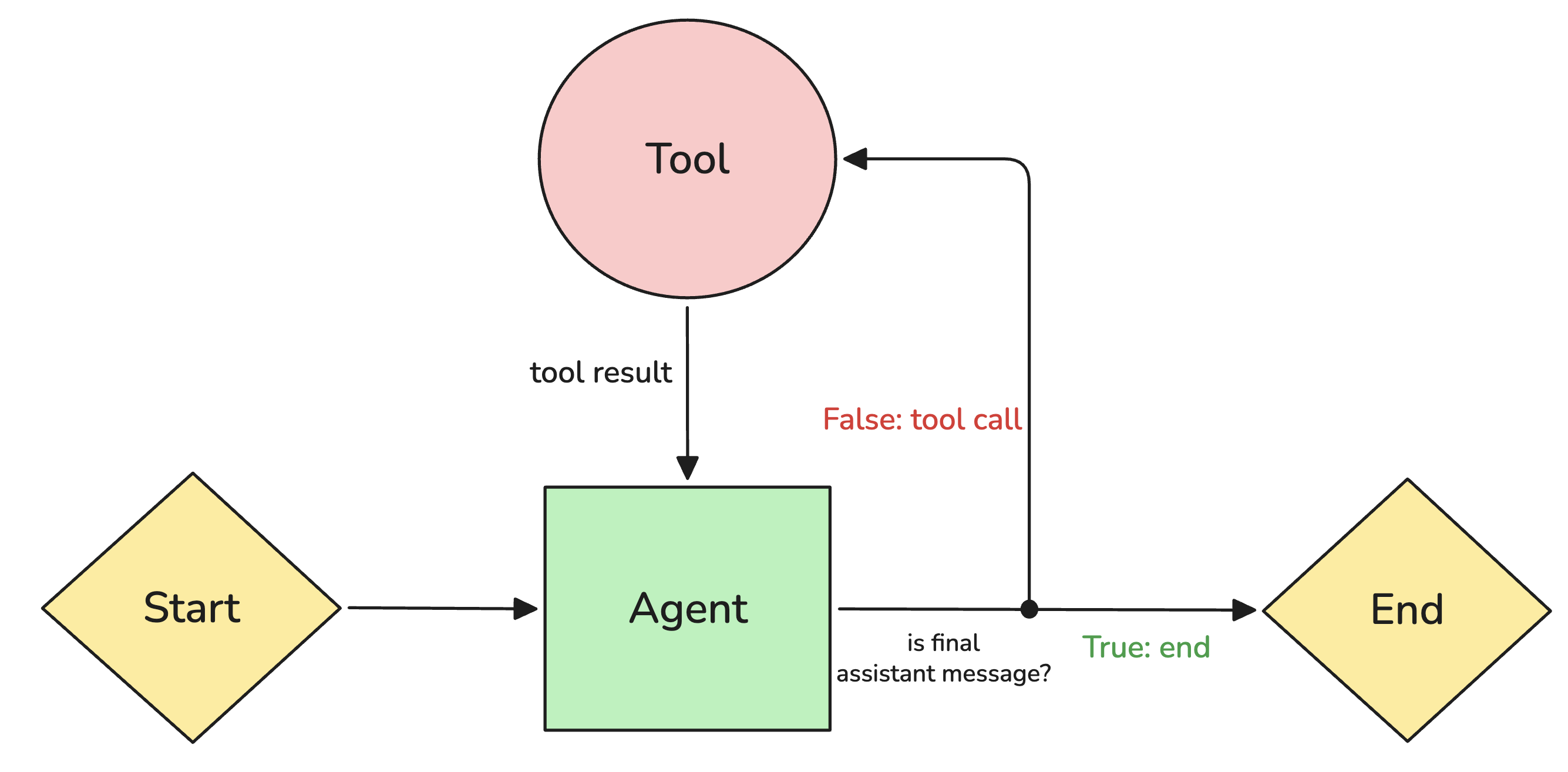
We support two reinforcement-learning modes with tools:
- Single-turn: The agent calls tools only once and then generates the response.
- Multi-turn: The agent calls tools several times and then generates a response after the last tool call.
You can define max_turns in config.yml to control how many tool calls the agent can make before generating its final response. Check out the rollout configuration for more information.
We allow users to define tools and stray away from complex context management for agent harnesses. Read our blog on reinforcement learning and agent harnesses to understand the rationale.
Step 1: Initialize the Template
We are going to train an agent to answer questions reliably by finding data using Wikipedia search.
To do this, let's first initialize the template. Make a new folder and create the template:
rnow init --template tutorial-toolWe have just generated train.jsonl, config.yml, rewards.py, tools.py, and requirements.txt.
We previously looked at train.jsonl and rewards.py; check out Your First Reward to understand how these files work.
The requirements.txt file lists Python packages required to run your rewards.py or tools.py.
Step 2: Define the Tool
In order to define an agent you have to define a tool the LLM can use. You do that similarly to reward functions: by decorating a function with @tool.
The tool must be typed, as the tool schema is inferred from its type annotations (learn what this means here).
Query from wikipedia
a. First, we send the request to Wikipedia's API and handle errors:
resp = requests.get("https://en.wikipedia.org/w/api.php", params={...}, timeout=10)
data = resp.json()b. Then we parse and return the results:
for item in data.get("query", {}).get("search", []):
results.append({"title": title, "link": link, "snippet": snippet})
return resultsComplete Example
Here's the full tools.py:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from rnow.core.tool import tool
@tool
def internet_search(query: str) -> dict:
"""Search the web and return up to 5 results (title, link, snippet)."""
try:
resp = requests.get("https://en.wikipedia.org/w/api.php",
params={"action": "query", "list": "search", "srsearch": query, "format": "json", "srlimit": 5},
headers={"User-Agent": "ReinforceNow/1.0 (training platform)"},
timeout=10)
resp.raise_for_status()
except requests.RequestException:
return []
data = resp.json()
results = []
for item in data.get("query", {}).get("search", []):
snippet = BeautifulSoup(item.get("snippet", ""), "html.parser").get_text()
title = item.get("title", "")
results.append({"title": title, "link": f"https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/{title.replace(' ', '_')}", "snippet": snippet[:200]})
return resultsStep 3: Start the Run
Now that you've written your tool, you can start training your agent.
rnow run